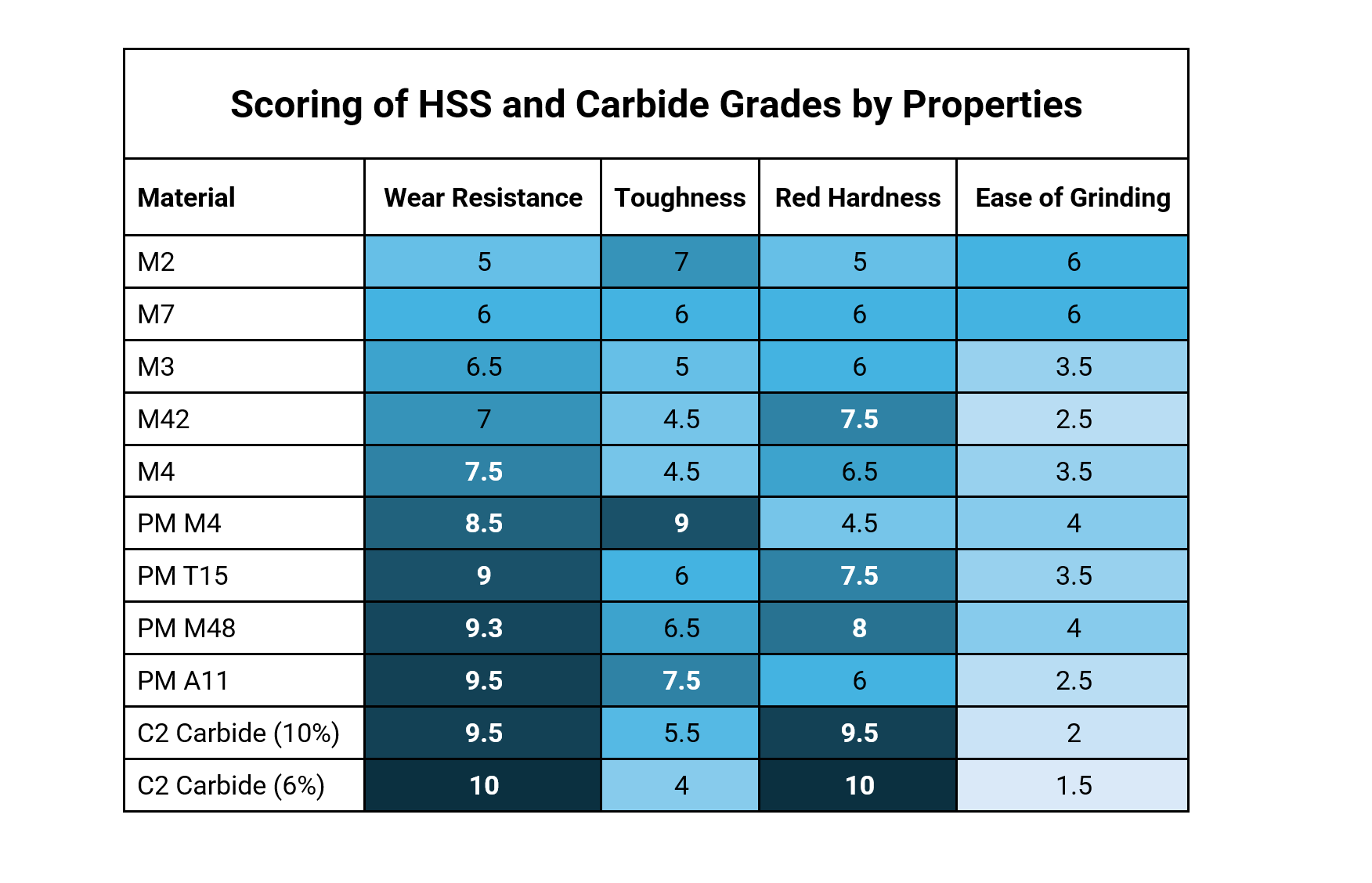
High Speed Steel and Carbide Grades
Choosing the right material for your cutting or reaming tools can significantly impact performance, efficiency, and tool life. Whether you're working with tough alloys or softer metals, each material grade has its own strengths and weaknesses. The table below is designed to help you identify the strengths and weaknesses of common High-Speed Steel (HSS) and carbide grades, to aid in choosing the one best suited for your application. Materials are scored on a 10-point scale, with higher values indicating a more desirable rating.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is a versatile, cost-effective tool material known for its toughness and ease of sharpening. It's ideal for general-purpose machining and can maintain cutting performance at moderate temperatures. Carbide, by contrast, is much harder and more wear-resistant, making it suitable for high-speed or high-volume applications—especially in abrasive or heat-intensive conditions—but it's also more brittle and less forgiving under impact.
Here's an overview of the properties measured:
- Wear Resistance: Ability to resist abrasion and maintain a sharp cutting edge over time.
- Toughness: Ability to withstand impact and resist chipping or breaking during use.
- Red Hardness: Ability to retain hardness and cutting ability at high temperatures.
- Ease of Grinding: How easily the material can be ground or resharpened.
M2 High Speed Steel
- Use for: General-purpose reaming, mild steel, low-carbon steel, aluminum
- Why: Good balance of wear resistance and toughness; economical choice
M3
- Use for: Carbon steels, cast iron, and bronze
- Why: Better wear resistance than M2, but not as common today due to newer alternatives
M42 (Cobalt HSS)
- Use for: Stainless steel, nickel alloys, Inconel, and work-hardening materials
- Why: High red hardness from cobalt; resists heat and dulling in tough materials
M4
- Use for: High-strength alloys, tool steels, medium-hard stainless
- Why: Higher wear resistance than M2
PM M4
- Use for: High-strength alloys, tool steels, medium-hard stainless
- Why: Powder metal version has superior toughness and edge stability compared to conventional M4
M7
- Use for: Softer steels and aluminum, especially where toughness is more critical than edge retention
- Why: Similar to M2 but with improved toughness
PM T15
- Use for: Heat-resistant alloys, stainless steels, titanium, and hard tool steels
- Why: Excellent hot hardness and wear resistance; useful for interrupted cuts or high cutting speeds
PM M48
- Use for: High-speed, high-pressure reaming in difficult-to-machine materials like Inconel or hardened steel
- Why: Superior hot hardness, toughness, and edge life at elevated temperatures
PM A11 (also known as CPM 10V)
- Use for: Highly abrasive materials like fiberglass composites, carbon fiber, cast iron
- Why: Exceptional wear resistance, good for long production runs or abrasive materials
C2 Carbide (10%)
- Use for: Graphite, cast iron, non-ferrous metals, fiberglass, hard plastics
- Why: Higher cobalt increases toughness but slightly reduces wear resistance
C2 Carbide (6%)
- Use for: Graphite, cast iron, non-ferrous metals, fiberglass, hard plastics
- Why: Extremely hard and wear-resistant, ideal for abrasive or high-volume reaming
Recommendations by Material Type
| Material Type | Typical Challenges | Recommended Grades |
|---|---|---|
| Mild / Carbon Steel | Built-up edge, general wear | M2, M7 |
| Cast Iron | Abrasive, brittle | PM A11, M3, C2 Carbide |
| Stainless Steel | Work-hardening, low thermal conductivity | M42, PM T15, PM M4 |
| Titanium / Inconel | Heat-resistant, gummy chips | PM M48, PM T15 |
| Aluminum / Brass | Built-up edge, soft | M2, M7, C2 Carbide (10%) |
| Fiberglass / Composites | Abrasive, delamination risk | PM A11, C2 Carbide |
| Tool Steels (Hardened) | High hardness, edge wear | PM M4, PM M48, C2 Carbide |